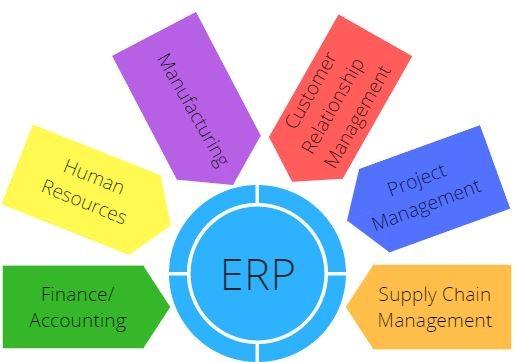
Each company is unique in terms of data managed through their ERP systems. Some businesses use ERP software for critical transactions and information about Finance, Accounting and Supply Chain Management. Other companies may use HR, Manufacturing, Customer Relationships, or Project Management as core ERP modules.
Time is of the essence in business. Spending years implementing and integrating a new ERP within a company is not acceptable. A lengthy implementation will allow competitors to overtake you, reduce your market share, and disrupt your company’s flow. Therefore, you should install your ERP system in a quick and successful manner.
So, how do you implement an ERP Application?
There are ten steps a company should follow during ERP implementation.
I. Project Scoping
The first phase of ERP implementation is scoping the project. The implementation team defines the scope and parameters. ERP implementation has two types of approaches:
Big bang or incremental. It is up to you which approach you should take.
The big bang approach involves rolling out the ERP to the entire company, including all the branches and sub-branches. The incremental approach means only using the ERP for a select few areas of the company before spreading out to the whole business. In both the cases, you need to decide if you will implement only a few modules or all of them. Discuss and come up with a strategy once you are ready to implement the project.
Once scoping finishes, start the analysis.
II. Business Analysis
Analysis is a crucial phase in the ERP project. Here, your company should examine and evaluate the business environment and processes. Define strategic and operational goals. Easy implementation should be your focus. You need to lower the priority of your current reports until advised of a status upgrade. Make sure you gather and collect the existing procedures, policies, and documentation. Also, hold interviews with management for additional information relating to the project.
Prepare a formal vision statement detailing the objectives and the design of the implementation.
Design is of two types: Technology and Architecture.
The Technology Design shows how to align the software and processes with the technology of your company to achieve the desired objectives.
The Architecture Design provides a framework for the commissioning and completion of the project. You also need to look at change management to see how worker performance, business practices, workflow, and reporting relationships gets affected.
Once you have analyzed, you need to decide the formal project kickoff date.
III. Implementation Kickoff
Announce the list of Executive Sponsors, Steering Committee and Project Team company wide. Hold a meeting to kick things off engaging and building enthusiasm among the participants. Through concept education, you can introduce the capabilities and expected benefits of the software. Establish a definitive timeline for the implementation.
Set up a war-room with communication tools and visual charts and ensure senior project stakeholders and sponsors have access to project updates at all times. Build trust between internal (company) and external (vendor) implementation teams. You should also establish the metrics to measure progress and set up the reporting and communication processes. You should have a general outline of the schedule for implementation along with basic milestones of the project. Once everyone is on the same page, you can work on the pilot.
IV. Pilot
Fourth phase is the Pilot. It is time to construct, test, assess, and refine the initial prototype aka pilot. Develop a pilot to use before introducing the ERP to a wider area. The team must identify a portion of the plant or product line to build this iteration on. Keep in mind that this prototype depends on the business goals, so it may not include all the application’s functionality. Once your team has built, tested and run the prototype, chart the results for logic and performance. Be sure your refinements are ongoing.
Consider using a project notebook to keep track of the progress. Also, hold prototype demonstrations for your executive sponsor sponsors, the steering committee and your key users. The core team of your company has to receive more training in the architecture and technology of the software. Discuss the capabilities, maintenance, and usage should and put them results into a test plan. This test plan needs to represent how you do business as a whole. Be sure to include any customization done to the system before you begin to build the ERP.
Step 0 – ERP Selection
There are things your company needs to do before you begin the ERP implementation.First, you should discover, examine, and assess your current business operations. If you don’t know where you stand now, it will be impossible to achieve your goals.
Based on your assessment, you will decide what ERP you are going to use. Selection of the ERP is a tedious process. Finding the right ERP takes time. Buying the wrong ERP is a costly affair. Some companies opt for a reliable third party software recommendation service like www.SoftwareHunt.in to help with the selection. Once you select it, you have to form a team that can work in a cohesive manner. Know what the key result areas are. You need to prepare for the implementation by defining goals and planning how you want the implementation to be carried out. Make sure you understand the requirements of your customers and the market so you can adapt. There are still six more stages in the process which we will cover in the next article.
Also read our blog “11 Mistakes made by SME’s while buying Business Software“

